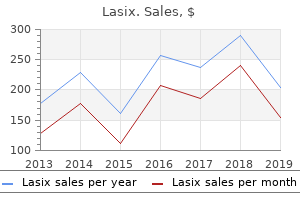
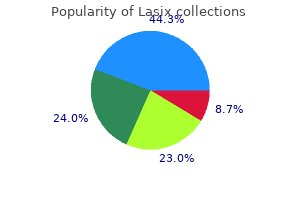
Lasix
"Lasix 40 mg sale, heart attack jokes."
By: Paul J. Gertler PhD
- Professor, Graduate Program in Health Management

https://publichealth.berkeley.edu/people/paul-gertler/
Rationale: A helper performs less than half the effort of lower body dressing (with a prosthesis considered a piece of clothing) blood pressure of normal person buy 100 mg lasix with mastercard. In contrast arrhythmia vertigo order lasix 100 mg online, coding level 04, Supervision or touching assistance, is used if the helper provides either verbal cues and/or only touching/steadying assistance as the resident completes the activity. F often drops her shoes and socks as she attempts to put them onto her feet or as she takes them off. Often a certified nursing assistant must first thread her socks or shoes over her toes, and then Mrs. U had his left lower leg amputated due to gangrene associated with his diabetes mellitus and he has reduced sensation and strength in his right leg. U has reduced sensation in his hands and limited upper body strength, but assists with the transfer. The physical therapist assists him in side scooting by lifting his buttocks/trunk in a rocking motion across the transfer board and into the wheelchair. In the event of inclement weather or if an indoor car simulator or outdoor car is not available during the entire 3-day assessment period, then use code 10, Not attempted due to environmental limitations. A therapyphysical therapist assistant guides and steadies the shaking, rolling walker forward while cueing Mr. T walks 50 feet with the therapist providing trunk support and the therapy assistant providing supervision. R is very motivated to use his motorized wheelchair with an adaptive throttle for speed and steering. R for frequent readjustments of his hand position to better control the steering and speed throttle. R often drives too close to corners, becoming stuck near doorways upon turning, preventing him from continuing to mobilize/wheel himself. A has a cardiac condition with medical precautions that do not allow him to participate inpropel his own wheelchair mobilization. A is completely dependent on a helper to wheel him 150 feet using a manual wheelchair. If codes 113 do not apply, use code 14, "Other Medical Condition," and proceed to I0020A. The hip fracture resulting in the total hip replacement is also documented in the medical record in the discharge summary from the acute care hospital. She also received regular blood glucose monitoring and treatment with insulin when she became hyperglycemic. The hospital discharge diagnoses of idiopathic pancreatitis, hypertension, and malnutrition were incorporated into Mrs. Her principal diagnosis of pancreatitis was included in the summary from the hospital. The pain items assess the presence of pain, pain frequency, effect on function, intensity, management and control. Before being assisted back into her chair, an range of motion assessment was completed that indicated no injury. This injury is noted by the physician to be attributed to the recent fall that occurred during the look-back period of the Quarterly assessment. Original Coding: J1900B, Injury (except major) wasis coded 1, one and J1900C, Major Injury is coded 0, none. For example, J2810, Genitourinary surgery - the kidneys, ureter, adrenals, and bladder-open, laparoscopic, includes open or laparoscopic surgeries on the kidneys, ureter, adrenals, and bladder, but not other components of the genitourinary system. Specific documentation may be found in progress notes, most recent history and physical, transfer notes, hospital discharge summary, etc. H was hospitalized for severe back pain from a compression fracture of a lumbar vertebral body, which was caused by her age-related osteoporosis. In addition, she has moderate congestive heart failure, is moderately overweight, and has hypothyroidism.
Possible correlation between Borna disease virus infection and Japanese patients with chronic fatigue syndrome arrhythmia magnesium generic lasix 40 mg. High incidence of antibodies to 5-hydroxytryptamine arteria inominada order lasix 40 mg on-line, gangliosides and phospholipids in patients with chronic fatigue and fibromyalgia syndrome and their relatives: Evidence for a clinical entity of both disorders. Markers of viral infection in monozygotic twins discordant for chronic fatigue syndrome. Health status in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and in general population and disease comparison groups. Viral persistence in the myocardium is associated with progressive cardiac dysfunction. Stress management skills, neuroimmune processes and fatigue levels in persons with chronic fatigue syndrome. A paradigm linking herpesvirus immediate-early gene expression apoptosis and myalgic encephalomyelitis chronic fatigue syndrome. Abortive lytic Epstein-Barr virus replication in tonsil-B lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis and a subset of the chronic fatigue syndrome. IgM serum antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus are uniquely present in a subset of patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome. Subset-directed antiviral treatment of 142 herpesvirus patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Antibody to Epstein-Barr virus deoxyuridine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase and deoxyribonucleotide polymerase in a chronic fatigue syndrome subset. Clinical, epidemiologic, and virologic studies in four clusters of the chronic fatigue syndrome. Detection of antibody against Borna disease virus-p24 in the plasma of Chinese patients with chronic fatigue syndrome by western-blot analysis. Relationships of cognitive difficulties to immune measures, depression and illness burden in chronic fatigue syndrome. A systematic review and critical evaluation of the immunology of chronic fatigue syndrome. Chronic fatigue syndrome is accompanied by an IgM-related immune response directed against neopitopes formed by oxidative or nitrosative damage to lipids and proteins. Simultaneous measurement of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus, human herpesvirus 6, herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, and 14 enteroviruses in chronic fatigue syndrome: Is there evidence of activation of a nonspecific polyclonal immune response? Low-dose hydrocortisone for treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Chronic musculoskeletal pain in patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome: A systematic review. Immunological similarities between cancer and chronic fatigue syndrome: the common link to fatigue? Endogenous pain modulation in response to exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and comorbid fibromyalgia, and healthy controls: A doubleblind randomized controlled trial. Cardiac function fluctuates during exacerbation and remission in young adults with chronic fatigue syndrome and "small heart. Renin-aldosterone paradox in patients with myalgic encephalomyelitis and orthostatic intolerance. Randomized clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of valganciclovir in a subset of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Postinfectious and chronic fatigue syndromes: Clinical experience from a tertiary-referral centre in Norway. Chronic fatigue syndrome after giardia enteritis: Clinical characteristics, disability and long-term sickness absence. Exercise and sleep deprivation do not change cytokine expression levels in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Association between serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and chronic fatigue syndrome. Evidence of actively replacing Epstein-Barrvirus in patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome.
40 mg lasix amex. Next Level Dab Making: Rosin Presses.
Because cold temperature improves the weakness of myasthenia arteria sacralis mediana buy lasix 100mg free shipping, the positive result is diminished ptosis after application of the ice peak pulse pressure qrs complex lasix 100 mg for sale. When a person leans to one side, his or her head and eyes normally compensate by rotating in the opposite direction. For example, in the skier in the top figure, whose body is leaning to the right, the natural compensatory movements are tilting of the head to the left, elevation of the right eye and depression of the left eye, and torsion of both eyes (right eye intorts and left eye extorts), all movements that restore the normal vertical position of the head and eyes (left side of figure). All of these compensatory movements are part of the ocular tilt reaction, a normal reflex that stabilizes retinal images and is mediated by the otolith organs (especially the gravity-sensing utricle and its connections to the ocular motor nuclei and the vestibulospinal tract). Skew deviation (bottom figure) is the abnormal heterotropia that appears in disorders (especially cerebellar or brainstem lesions) that produce asymmetry in these pathways. The ice was applied to the eye for 2 minutes2224 or 5 minutes20 before determining the results of the test. Major causes are ischemic infarcts (all three nerves), intracranial aneurysms (especially the third cranial nerve), head trauma (especially the fourth cranial nerve), and tumors (especially when more than one of these nerves are affected). At least one-fourth of isolated cranial neuropathies affecting these nerves remain idiopathic, even in the modern era of clinical imaging. Seventy-five percent of ischemic mononeuropathies resolve within 4 months; persistence beyond this should prompt evaluation for other causes. Complete third nerve palsy (of the left eye in this example) causes ptosis that obscures the position of the eye (first row). When the lid is held open (by a piece of tape in this example), the eye appears deviated outward and slightly downward (second row), because of unopposed action of the lateral rectus muscle (abducting the eye) and superior oblique muscle (depressing the eye). In this example of third nerve palsy, the pupil is dilated because the cause is an intracranial aneurysm: Many ischemic third nerve palsies spare the pupil. When the patient looks to the right (fourth row), the left eye fails to adduct past the midline. Pupil-SparingRule41,42 the most common identified causes of isolated nontraumatic third nerve paralysis are posterior communicating artery aneurysm (which must be managed aggressively) and ischemic infarction of the third nerve (which is managed conservatively). In over 95% of aneurysmal palsies, the pupil reacts sluggishly to light or is fixed and dilated, but in 73% of ischemic palsies, the pupil is spared. The rule applies only to patients with complete paralysis of the ocular muscles of the third nerve and complete sparing of the pupil. Up to 4% of patients with aneurysms do have sparing of the pupil, although the third nerve muscles are only partially paralyzed. The rule should be applied sparingly to patients aged 20 to 50 years, an age-group in which ischemic infarcts are uncommon. Nonetheless, the pupil-sparing rule had greater value in an earlier era when the only diagnostic test for intracranial aneurysms was catheter angiography (a test carrying a 2% risk of stroke), a time when clinicians sought ways to identify who could safely avoid this potentially dangerous test. Today, with the availability of safer noninvasive testing methods (computed tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance imaging), some experts recommend noninvasive vascular imaging of all patients with new-onset isolated nontraumatic third nerve palsies, whether or not the pupil is spared. ClinicalSyndromes Associated findings distinguish the different causes of third nerve palsy. Ipsilateral Brainstem Damage Damage to the third nerve fascicle as it exits the ipsilateral brainstem causes accompanying ipsilateral cerebellar signs (Nothnagel syndrome, involving the superior cerebellar peduncle), contralateral hemitremor (Benedikt syndrome, involving the red nucleus), or contralateral hemiparesis (Weber syndrome, involving the cerebral peduncle). Damage to the Nerve in the Subarachnoid Space Important causes include uncal herniation. Tilting the head aggravates the diplopia because it requires the ipsilateral eye to intort, which calls upon simultaneous contraction of the superior oblique and superior rectus muscles. These two muscles work together, and the tendency of the superior oblique muscle to depress the eye is normally balanced by that of the superior rectus muscle to elevate the eye. Absence of intorsion (which is apparent by observing the medial conjunctival vessels) indicates palsy of both the third and fourth nerves. HeadPosition Studies have shown that in patients with isolated third nerve palsies, 45% actually habitually tilt their head away from the side of the lesion (to minimize any need for intorsion in the affected eye). As expected, when the head is tilted toward the affected side, the diplopia and hypertropia worsen in 96% of patients.
The clavicle mainly acts as a brace holding the scapulae and the arms up and away from the ribs heart attack damage trusted lasix 40 mg. It also enables us to raise our hands by allowing the scapula to slip forward and back (Tortora & Derrickson arteria arcuata discount 40mg lasix amex, 2008). At the end of the radius and ulna lie the carpals, collectively referred to as the wrist. While most people consider their wrist to be located between the hand and lower arm, the true wrist, the carpus, exists at the base of the hand. The palm of the hand is supported by the metacarpals, while the three phalanges make up the fingers. The rest of the body could not be connected to the lower extremities without the existence of one structure: the pelvis. The two ring-shaped portions located inferior to the hip sockets are called ischium while the femur refers to the bone in the thigh. The patella (kneecap) guards the knee joint against blows and improves leverage of thigh muscles which raise the lower leg. These tibiofibular joints, unlike the joints of the radius and ulna, do not allow for much movement. Of these bones, only the tibia bears weight the fibula serves only as an attachment place for muscles. The calcaneus forms the heal of the foot, while the talus connects the foot with the tibia and fibula. Cartilage is a type of dense connective tissue composed of cells called chondrocytes which are dispersed in a firm gel-like ground substance, called the matrix. It is avascular (contains no blood vessels) and nutrients are diffused through the matrix. Cartilage is found in the joints, rib cage, ear, nose, throat, and between intervertebral disks (Tortora & Derrickson, 2008). Because all movement requires muscles, they are located in practically every region of the body. Muscles are distinct from all other tissues because of their unique ability to contract (Adams, 2004). In one motor unit as few as two to three muscle fibers or as many as 2,000 fibers exist. The upper and lower extremities are almost entirely made up of muscles, and over forty muscles are located in the skull alone. Blood vessels streaming through the muscles provide them with nutrients and oxygen while removing waste products. Nerves deliver signals that cause muscles to contract and relax resulting in movements as delicate as a blink of the eyelid or as powerful as a punch of the fist. Skeletal muscle Roughly 630 skeletal muscles are found in the body accounting for approximately 50% of male body weight and 40% of female body weight. Skeletal muscle tissue is the strongest and hardest working in the body and is also its longest form of muscle. Skeletal muscle tissue is known as striated muscle tissue because muscle tissue, which crosses over each fiber, causes an appearance of crisscrossing. Though fragile, skeletal muscle tissue is very strong because it is protected by a sheath. Interestingly, skeletal muscle tissue is also the only type of muscle tissue that is voluntary. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and is commonly found in hollow organs such as the stomach, bladder, and respiratory passages. Typically, two layers run together, alternately contracting to change the size of the organ. Cardiac muscle Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the heart; it is striated, involuntary, and responsible for pumping blood throughout the heart. These connecting structures of bones are classified either according to degree of movement or type of connective tissue that joins them. Fibrous joints are those ends of bones connected by fibrous tissue without joint cavity; they are capable of little or minimum movement. Synovial joints have joint cavities where the fibrous connective tissue hold the bones together.
References:
- https://www.michigan.gov/documents/mdch/Tetanus_388983_7.pdf
- https://www.wlwv.k12.or.us/cms/lib/OR01001812/Centricity/Domain/1341/NOTES%20-%20CH%2017_Evolution%20of%20Populations%202015.pdf
- https://repository.library.georgetown.edu/bitstream/handle/10822/557559/Diehl_georgetown_0076M_11958.pdf?sequence=1
- https://www.asn-online.org/education/training/fellows/HFHS_CKD_V6.pdf